For this I am using the raspbx-10 which seems to be stable at the moment I do this. The Pi I use is my old model 3 B, but should definetly work on model 4. Aslo I use the current updated SCCP Manager which has a bug. Hopefully the bug will be fixed at the time you read this post but anyhow I will provide a simple work around I did myself to overcome it.
I am writing this post after trying numerous ways to do this using SIP and SCCP but looks like Cisco SIP images were full of bugs and this was the method which worked for me. Note that the phones I use here are very old but this method will do the trick for any Cisco phone model you have and this seems to be the easiest way.
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
apt-get install git
cd /usr/src
git clone https://github.com/chan-sccp/chan-sccp chan-sccp
cd chan-sccp
./configure --enable-conference --enable-video
Now go to Admin -> Asterisk Modules and under Excluded Modules add chan_skinny.so and under Manually Loaded Modules add chan_sccp.so and hit Apply Config..
Under Admin -> Module Admin, use Upload Modules to upload the downloaded file.
Now click Manage local modules -> SCCP Manager, hit Install and Process, Confirm..
If you get this error, just go to the cli and hit the following command to edit the php file.
nano /var/www/html/admin/modules/sccp_manager/install.php
Now Plug the phones to the switch and give the hard reset.
Option 150 must be configured to identify the TFTP server..
Download the image from official site and fireup a an SD card and load it to the Raspberry Pi.
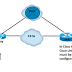
Lab setup is simple, all the devices are in the same LAN. DCHP server is created in a router, TFTP is hosted by default in FreePBX server which again is inside my Pi.
Once the RasPBX is installed, log in using the root username and password and set it up with a static IP.
apt-get install git
cd /usr/src
git clone https://github.com/chan-sccp/chan-sccp chan-sccp
cd chan-sccp
./configure --enable-conference --enable-video
make -j2 && make install
Now just use a web browser to access log in to FreePBX and do the initial configuration.
Just give a username and password, an email and a System ID name..
Then use the above given password to log in to the FreePBX Administration on next window.
Just give a username and password, an email and a System ID name..
Then use the above given password to log in to the FreePBX Administration on next window.
Now hit a reboot in CLI..
Download the SCCP Manager from following link..
Under Admin -> Module Admin, use Upload Modules to upload the downloaded file.
Now click Manage local modules -> SCCP Manager, hit Install and Process, Confirm..
Here is the place you get the following error.
If you get this error, just go to the cli and hit the following command to edit the php file.
nano /var/www/html/admin/modules/sccp_manager/install.php
just comment the if clause and save it like below.
Now Process, Confirm it again it will be fine, just hit Return..
Now you can see new SCCP Connectivity Tab appear in the PBX.
Go to SCCP Connectivity -> Server Config and set SCCP Server Name to Asterisk.
Go to SCCP Connectivity -> Server Config and set SCCP Server Name to Asterisk.
Move to SCCP Device and Change the Digit Timeout to 2 which is more practical for lab.
Move to SCCP Time and check Yes to NTP Server Enabled and change the Time Zone to match yours..
Hit Submit and Apply Config..
Hit Submit and Apply Config..
Now download the images from Cisco official site. The phone model I am using is 7945G.
I used version Firmware version 9.4(2)SR4 which is kind of a latest. Make sure to download the .zip file not the cop.sgn file.
Now unzip the files and load them to /tftpboot directory using a SFTP client like FileZilla.
Following are the firmware files.
Following are the firmware files.
Now go back to SCCP Connectivity -> System Parameters and select Show All from drop down.
Search for 7945 and hit the Pencil mark in Actions.
Copy the Load Image name from the actual file name and paste it (without .loads extension) and hit Apply.
Now go to Sccp Connectivity Tab -> Phones Manager. Click Add Extension.
In General Tab, I entered this phone Extension and Display Name both to be 1001 and hit Submit.
Again go to SCCP Manager -> SCCP Phone and click Add Device Phone.
Under Device Configuration, enter the MAC address of the phone and Type to match something like 7940 (7945 was not there). Also I changed the device label to be 1001. The label has nothing to do with the extension.
Under Device Configuration, enter the MAC address of the phone and Type to match something like 7940 (7945 was not there). Also I changed the device label to be 1001. The label has nothing to do with the extension.
The Line is mapped at the Device Buttons tab..
Hard reset is giving power pressing the # key until the line buttons blink and then push 123456789*0#
Then the phones will register..
Please note that the following is the DHCP configuration in my router.